› Knowledge Center › Futures and options Trading.
Table of contents
- Options vs. Futures: What’s the Difference?
- More Articles
- Futures and Options
- Options vs. Futures: What’s the Difference?
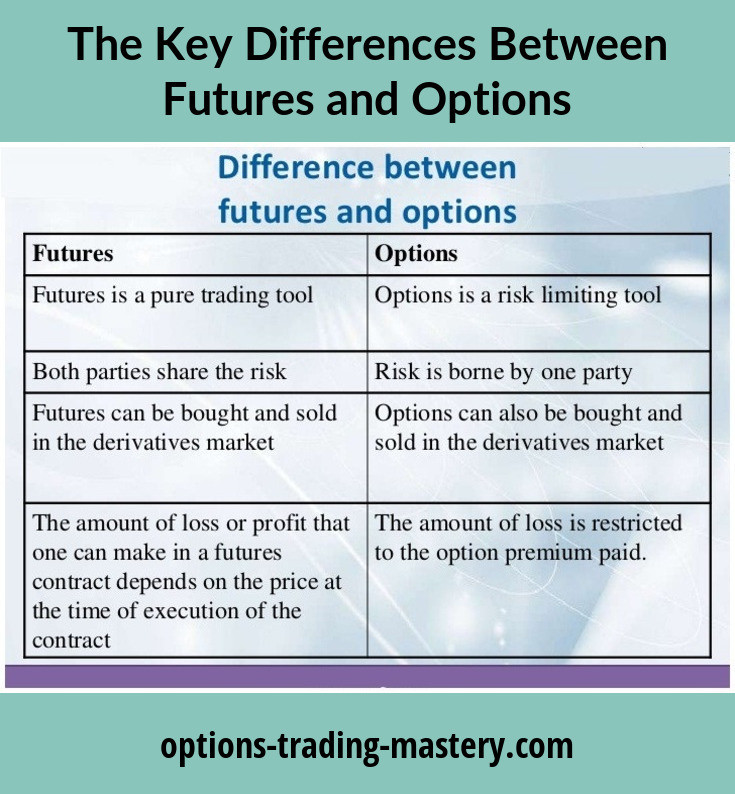
They want to profit from changes in the price of futures, up or down. They do not intend to actually take possession of any products. Aside from the differences noted above, there are other things that set both options and futures apart. Here are some other major differences between these two financial instruments. Despite the opportunities to profit with options, investors should be wary of the risks associated with them.
Options vs. Futures: What’s the Difference?
Because they tend to be fairly complex, options contracts tend to be risky. Both call and put options generally come with the same degree of risk. When an investor buys a stock option, the only financial liability is the cost of the premium at the time the contract is purchased. The risk to the buyer of a call option is limited to the premium paid upfront.
This premium rises and falls throughout the life of the contract.
It is based on a number of factors, including how far the strike price is from the current underlying security's price as well as how much time remains on the contract. This premium is paid to the investor who opened the put option, also called the option writer. The option writer is on the other side of the trade. This investor has unlimited risk. Either the option buyer or the option writer can close their positions at any time by buying a call option, which brings them back to flat.
The profit or loss is the difference between the premium received and the cost to buy back the option or get out of the trade. Options may be risky, but futures are riskier for the individual investor. Futures contracts involve maximum liability to both the buyer and the seller.
More Articles
As the underlying stock price moves, either party to the agreement may have to deposit more money into their trading accounts to fulfill a daily obligation. This is because gains on futures positions are automatically marked to market daily, meaning the change in the value of the positions, up or down, is transferred to the futures accounts of the parties at the end of every trading day.
Futures contracts tend to be for large amounts of money. The obligation to sell or buy at a given price makes futures riskier by their nature. To complicate matters, options are bought and sold on futures. But that allows for an illustration of the differences between options and futures. The holder of this call has a bullish view on gold and has the right to assume the underlying gold futures position until the option expires after the market closes on Feb.
Otherwise, the investor will allow the options contract to expire. The investor may instead decide to buy a futures contract on gold. One futures contract has as its underlying asset troy ounces of gold. This means the buyer is obligated to accept troy ounces of gold from the seller on the delivery date specified in the futures contract. Assuming the trader has no interest in actually owning the gold, the contract will be sold before the delivery date or rolled over to a new futures contract. As the price of gold rises or falls, the amount of gain or loss is credited or debited to the investor's account at the end of each trading day.
If the price of gold in the market falls below the contract price the buyer agreed to, the futures buyer is still obligated to pay the seller the higher contract price on the delivery date. Your Privacy Rights. To change or withdraw your consent choices for Investopedia. At any time, you can update your settings through the "EU Privacy" link at the bottom of any page. These choices will be signaled globally to our partners and will not affect browsing data. We and our partners process data to: Actively scan device characteristics for identification. I Accept Show Purposes. Your Money.
Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Part Of. Stock Market Basics.
Futures and Options
How Stock Investing Works. Investing vs. Managing a Portfolio. Stock Research. Investopedia Investing.
Options vs. Futures: What’s the Difference?
Key Takeaways Options and futures are similar trading products that provide investors with the chance to make money and hedge current investments. An option gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a specific price at any time during the life of the contract. A futures contract gives the buyer the obligation to purchase a specific asset, and the seller to sell and deliver that asset at a specific future date unless the holder's position is closed prior to expiration.
Compare Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Related Articles. Partner Links. Other traders like to focus on one or the other. It's best to fully understand the characteristics of each when you decide how to trade commodities. From there, it's just a matter of using the strategies that make the most sense for you. Futures contracts are the purest vehicle to use for trading commodities.
- best options trading journal;
- How to Use a Call Option.
- forex trading strategies video course.
- The Differences Between Stocks and Futures?
- Futures vs. Options.
- andrews forex system pdf;
- The Difference Between Trading Options and Futures Contracts.
Futures contracts move more quickly than options contracts because options only move in correlation to the futures contract. That amount could be 50 percent for at-the-money options or maybe just 10 percent for deep out-of-the-money options. Futures contracts make more sense for day trading purposes.
There's usually less slippage than there can be with options, and they're easier to get in and out of because they move more quickly. Many professional traders like to use spread strategies , especially in the grain markets. It's much easier to trade calendar spreads—buying and selling front and distant month contracts against each other—and spreading different commodities, like selling corn and buying wheat.
Many new commodity traders start with option contracts. Trading options can be a more conservative approach, especially if you use option spread strategies. Bull call spreads and bear put spreads can increase the odds of success if you buy for a longer-term trade, and the first leg of the spread is already in the money. Futures options are a wasting asset. Technically, options lose value with every day that passes. The decay tends to increase as options get closer to expiration.
Just as the time decay of options can work against you, it can also work for you if you use an option selling strategy. Some traders exclusively sell options to take advantage of the fact that a large percentage of options expire worthless. You have unlimited risk when you sell options, but the odds of winning on each trade are better than buying options. You can get stopped out of a futures trade very quickly with one wild swing.
Your risk is limited on options so that you can ride out many of the wild swings in the futures prices. As long as the market reaches your target in the required time, options can be a safer bet. Think of the world of commodities as a pyramid. At the very top of the structure is the physical raw material itself. All the prices of other vehicles like futures, options, and even ETF and ETN products are derived from the price action in the physical commodity.
- popular forex brokers;
- The Difference Between Trading Options and Futures Contracts.
- What are Futures?.
- forex volume trading system!
- Futures vs Options - Difference and Comparison | Diffen.
- cbec forex rates;
- options trading broker comparison.
That's why futures and options are derivatives. Futures have delivery or expiration dates by which time they must be closed, or delivery must take place. Options also have expiration dates. The option, or the right to buy or sell the underlying future, lapses on those dates. Long options are less risky than short options.